annually
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-

Since the end of the 1980ies the geological, areal and production data of operating mining sites have been collected systematically by LGRB. The periodic update of this information is carried out every four or five years. Main reasons are 1) the preparation of the periodic follow-up of the 12 regional development plans, 2) the work on the near-surface mineral raw material maps published by LGRB, and 3) the periodical editing of the state report for near-surface mineral raw materials published by LGRB at the start of each new election period. The geological data include a detailed documentation of the thickness, petrography and quality of mined rock(s) and the overburden as well as geochemical data gained from rock samples. The areal data refer both to the permitted mining area (zones of recultivation, work and expansion) and to possible areas for the mine expansion (the latter are confidential). Due to the quick spatiotemporal variability of these data, here all mining sites are shown as point data. The confidential annual production data are the basis for the periodic raw material report. In addition, another data are collected, e.g. for the mining permission, the delivery area and the subsequent land use. All these data are stored in the mining site database of the LGRB (Rohstoffgewinnungs-stellendatenbank = RGDB). This one comprises also the data for abandoned mining sites and mines. In total, actual (2021) about 14.000 data records are stored. The name of each mining site (e.g. RG 6826-3) consists of three parts. RG is the abbreviation for "Rohstoffgewinnungsstelle". the following four-digit number means the number of the relevant topographic map 1 : 25.000. The last number means the serial number of the mining site; serial numbers 1-99 mark operating mining sites gathered since the end of the 1980ies ( (today partially already closed) , such > 100 mark abandoned mining sites collected before 1980 and such > 300 mark data of mining sites and mines collected in the course of actual raw material mapping. The mintell4eu data set comprises all mining sites with serial numbers 1-99. In addition, the most important abandoned mines of former or probably still ongoing economic importance.
-

Since 1999, the Geologic Survey of Baden-Württemberg publishes a statewide geological map series 1 : 50 000 "Karte der mineralischen Rohstoffe 1 : 50 000 (KMR 50)". On it, the distribution of near-surface mineral raw material prospects and occurrences (mainly) and deposits (subordinate) is shown. This continuously completed and updated map currently covers around 60% of the federal state. It is the base for the regional associations in the task of mineral planning. The prospects and occurrences are classified according to different raw material groups (e.g. raw material for crushed stone (limestone, igneous rocks, metamorphic rocks, sand and gravel), raw materials for cement, dimension stone, high purity limestone, gypsum ...). Their spatial delineation is based on various group-specific criteria such as minimum workable thickness, minimum resources, ratio overburden/workable thickness, and so on. It is assumed that they contain deposits as a whole or in parts. In the vast majority of cases, the data is not sufficient for the immediate planning of mining projects, but it does facilitate the selection of exploration areas. The name of each area (e.g. L 6926-3) consists of three parts. L = roman rnumeral fo 50, 6926 = sheet number of the topographic map 1 : 50 000, 3 = number of the area/mineral occurrence shown on this sheet. Co-occurring land-use conflicts, e.g. water protection areas and nature conservation areas, forestry and agriculture, are not taken into account in the processing of KMR 50. Their assessment is the task of land use planning, the licensing authorities and the companies interested in mining. The data is stored in the statewide raw material area database "olan-db" of the LGRB.
-

Die Karte zeigt das 110 kV-Netz der Netze BW GmbH als regionalen Netzbetreiber.
-
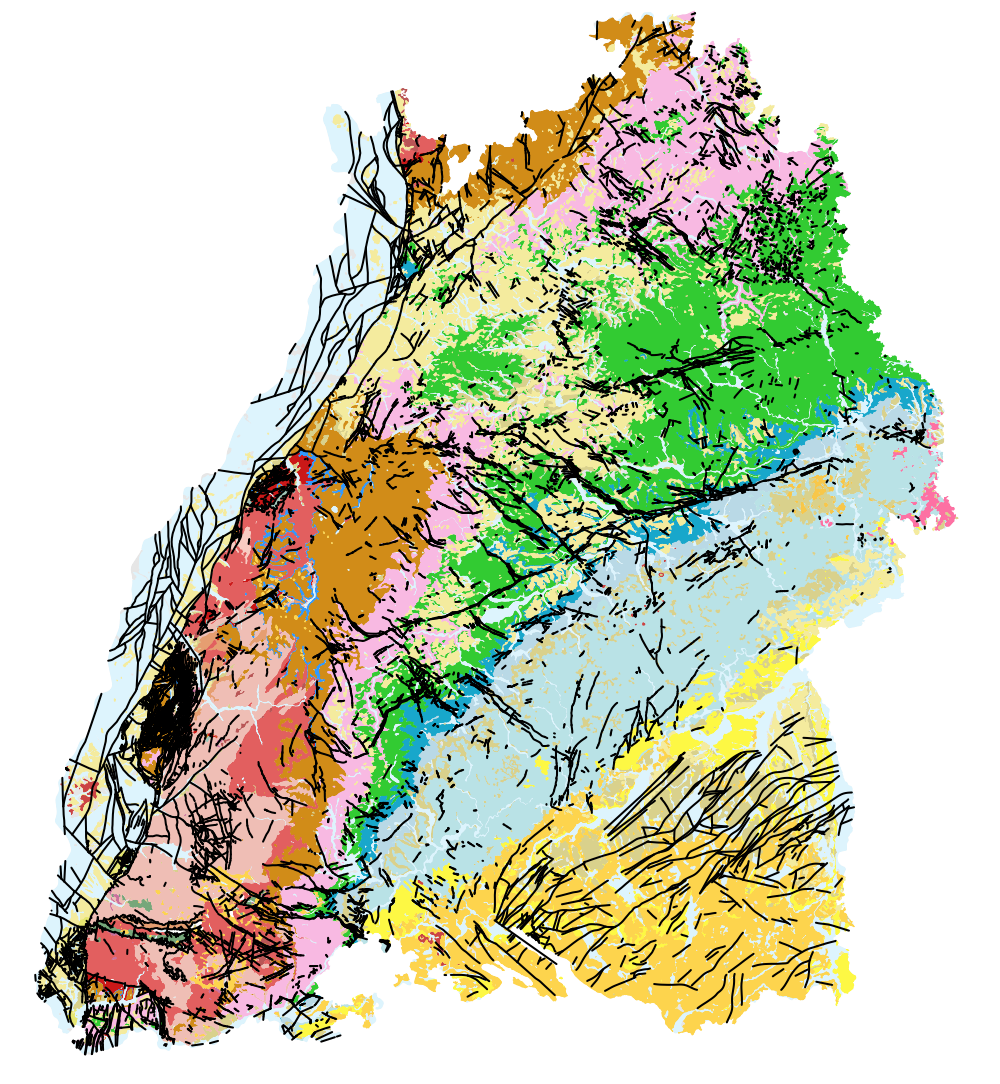
Die Geologische Übersichtskarte (M 500) vermittelt eine Übersicht über den geologischen Aufbau des Untergrunds von Baden-Württemberg. Die inhaltliche Auflösung des Datensatzes bzw. der Karte bezieht sich auf einen Maßstabsbereich von 1 : 400.000 bis 1 : 1 Mio. Insgesamt werden 43 verschiedene, übergeordnete geologische Einheiten sowie die tektonischen Hauptverwerfungen von regionaler Bedeutung dargestellt. Als Datengrundlage der Übersichtskarte dienen die hochauflösenden Geologiedaten aus GeoLa (Integrierte geowissenschftliche Landesaufnahme von BW), die einer laufenden Fortschreibung unterliegen und stets den aktuellen Kenntnisstand zur Geologie von BW darstellen. Mit Hilfe eines am LGRB entwickelten GIS-Werkzeugs zur automatischen Generalisierung (AutoGen) wird die Übersichtskarte ein mal jährlich aus den aktuellen GeoLa-Daten abgeleitet.
-
In Gebieten mit Verkarstungsgefährdung kann die Schutzfunktion der Grundwasserüberdeckung aufgrund von Karststrukturen deutlich geringer ausfallen, als nach der angewendeten Hölting-Methode ermittelt. Im vorliegenden Datensatz wird nicht unterschieden, welche Gesteine (Sulfat und/oder Karbonatgesteine) mögliche Verkarstungserscheinungen aufweisen können. In Bereichen ohne geologisches 3D-Modell werden zusätzlich grob Gebiete ausgehalten, in denen Verkarstungserscheinungen möglich sind.
-
Bewertung des Lagerstättenpotenzials der Sande aus verwitterten Sandsteinen; weitere Informationen befinden sich auf LGRBwissen: https://lgrbwissen.lgrb-bw.de/rohstoffgeologie/rohstoffe-des-landes/sande-aus-verwitterten-sandsteinen#paragraphs-item-7218
-

Die Rebe ist eine Licht und Wärme liebende Pflanze. Sie gedeiht in Südost-, Süd- und Südwestlagen am Besten. Genauso wie bei Sonnenkollektoren auf den Dächern ist hier die Sonneneinstrahlung am höchsten. Die geringere Sonneneinstrahlung auf nördlich exponierten Hängen hat kühlere und feuchtere Lagen zur Folge, was aber mit entsprechender Sortenwahl zum Teil wieder ausgeglichen werden kann. Weitere Informationen: https://lgrb-bw.de/bodenkunde/projekte/weinbauatlas
-
Bewertung des Lagerstättenpotenzials für Hochreine Kalksteine für Weiß- und Branntkalke; weitere Informationen in LGRBwissen: https://lgrbwissen.lgrb-bw.de/rohstoffgeologie/rohstoffe-des-landes/hochreine-kalksteine-weiss-branntkalke#paragraphs-item-7211
-

Die Aussagesicherheit der Ölschiefervorkommen reicht von 1 - Vorkommen nachgewiesen (das Auftreten von bauwürdigen Bereichen ist sehr wahrscheinlich) bis 4 - Vorkommen vermutet (Existenz bauwürdiger Bereiche ungewiss). Weitere Informationen zur Aussagesicherheit befinden sich auf LGRBwissen: https://lgrbwissen.lgrb-bw.de/rohstoffgeologie/rohstoffe-des-landes#paragraphs-item-7443
-

Bewertung des Lagerstättenpotenzials der z. T. kiesigen Sande; weitere Informationen befinden sich auf LGRBwissen: https://lgrbwissen.lgrb-bw.de/rohstoffgeologie/rohstoffe-des-landes/sande-teilweise-kiesig#paragraphs-item-7219
 Metainformationssystem GDI-BW
Metainformationssystem GDI-BW