Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
-

Since 1999, the Geologic Survey of Baden-Württemberg publishes a statewide geological map series 1 : 50 000 "Karte der mineralischen Rohstoffe 1 : 50 000 (KMR 50)". On it, the distribution of near-surface mineral raw material prospects and occurrences (mainly) and deposits (subordinate) is shown. This continuously completed and updated map currently covers around 60% of the federal state. It is the base for the regional associations in the task of mineral planning. The prospects and occurrences are classified according to different raw material groups (e.g. raw material for crushed stone (limestone, igneous rocks, metamorphic rocks, sand and gravel), raw materials for cement, dimension stone, high purity limestone, gypsum ...). Their spatial delineation is based on various group-specific criteria such as minimum workable thickness, minimum resources, ratio overburden/workable thickness, and so on. It is assumed that they contain deposits as a whole or in parts. In the vast majority of cases, the data is not sufficient for the immediate planning of mining projects, but it does facilitate the selection of exploration areas. The name of each area (e.g. L 6926-3) consists of three parts. L = roman rnumeral fo 50, 6926 = sheet number of the topographic map 1 : 50 000, 3 = number of the area/mineral occurrence shown on this sheet. Co-occurring land-use conflicts, e.g. water protection areas and nature conservation areas, forestry and agriculture, are not taken into account in the processing of KMR 50. Their assessment is the task of land use planning, the licensing authorities and the companies interested in mining. The data is stored in the statewide raw material area database "olan-db" of the LGRB.
-

Since the end of the 1980ies the geological, areal and production data of operating mining sites have been collected systematically by LGRB. The periodic update of this information is carried out every four or five years. Main reasons are 1) the preparation of the periodic follow-up of the 12 regional development plans, 2) the work on the near-surface mineral raw material maps published by LGRB, and 3) the periodical editing of the state report for near-surface mineral raw materials published by LGRB at the start of each new election period. The geological data include a detailed documentation of the thickness, petrography and quality of mined rock(s) and the overburden as well as geochemical data gained from rock samples. The areal data refer both to the permitted mining area (zones of recultivation, work and expansion) and to possible areas for the mine expansion (the latter are confidential). Due to the quick spatiotemporal variability of these data, here all mining sites are shown as point data. The confidential annual production data are the basis for the periodic raw material report. In addition, another data are collected, e.g. for the mining permission, the delivery area and the subsequent land use. All these data are stored in the mining site database of the LGRB (Rohstoffgewinnungs-stellendatenbank = RGDB). This one comprises also the data for abandoned mining sites and mines. In total, actual (2021) about 14.000 data records are stored. The name of each mining site (e.g. RG 6826-3) consists of three parts. RG is the abbreviation for "Rohstoffgewinnungsstelle". the following four-digit number means the number of the relevant topographic map 1 : 25.000. The last number means the serial number of the mining site; serial numbers 1-99 mark operating mining sites gathered since the end of the 1980ies ( (today partially already closed) , such > 100 mark abandoned mining sites collected before 1980 and such > 300 mark data of mining sites and mines collected in the course of actual raw material mapping. The mintell4eu data set comprises all mining sites with serial numbers 1-99. In addition, the most important abandoned mines of former or probably still ongoing economic importance.
-

This Downloadservice contains point locations of near-surface mineral raw material occurrences and mining sites in Baden-Württemberg (BW), which is one of 16 states of the Federal Republic of Germany. The information is harmonized according to the specifications of the MIN4EU database model as part of the Mintell4EU project. BW is rich in near-surface mineral raw materials. The most important are 1) Quaternary sands and gravels (Upper Rhine Graben Valley and glacial sediments of Upper Swabia), 2) Paleozoic rocks (mainly metamorphic rocks and granites, minor Permian volcanic rocks) in the Black Forest and the Odenwald, and 3) Middle Triassic (Southwest German scarplands) and Upper Jurassic (Swabian Alb) limestones. The deep-lying raw materials (various gangue ores, barite, fluorite, uranium ores), which were mined mainly in the Black Forest, are currently of no importance, with the exception of the still ongoing extraction of barite and fluorite in the Clara mine. In the future, some deposits could regain importance as raw material prices rise. Almost 100 million tons of mostly near-surface mineral raw materials are extracted annually in BW in currently about 500 mining sites (survey year: 2017). The annual raw material consumption is approx. 9 tons/inhabitant. At the beginning of the 2000s, there were still around 630 mining sites. This decline is due to both concentration processes and depletion of deposits. Since the end of the 1980ies the geological, areal and production data of operating mining sites have been collected systematically by LGRB. They are the basis for the periodic raw material report edited by LGRB and for the calculation of the need of mineral raw materials. Manly these pits, beside some important historic mines, are shown in the layer "MIN4EU LGRB-BW: mining sites - harmonized dataset". Another important task of the LGRB is to advise the regional planning authorities on securing mineral raw material supply. Beside the calculation of the need of mineral raw materials supply for the two planning periods (2 x 15 or 2x 20 years), the knowledge of mineral occurrences of proven or estimated economic value is important. After some preliminary stages, the LGRB is producing the Map of Mineral Resources in Baden-Württemberg 1 : 50,000 (KMR 50) as a basis and planning map for this purpose. On it, the distribution of near-surface mineral raw material prospects and occurrences (mainly) and deposits (subordinate) is shown. This continuously completed and updated map currently covers actually around 60% of the federal state. These occurrences are the topic of the second layer theme "MIN4EU LGRB-BW: near-surface mineral raw material occurrences - harmonized dataset".
-

Am LGRB wurde in den Jahren 2005 und 2006 eine digitales, dreidimensionales Übersichtsmodell des geologischen Untergrundes von Baden-Württemberg erstellt (3D-Landesmodell). Es zeigt neben den lithostratigraphischen Haupteinheiten überregionale Bruchstrukturen, junge vulkanische Bildungen wie Impaktkrater. Die aus dem 3D-Landesmodell abgeleiteten Mächtigkeitsverteilungen und Schichtlagerungskarten geben eine Übersicht über die Primär- und Restmächtigkeiten spätpaläozoischer, mesozoischer und känozoischer Einheiten und deren heutiger Raumlage. Neben einer Auswahl von Belegpunkten (Bohrungen, Aufschlüsse) werden der heutige Ausstrich und die Verbreitung im Maßstab 1:500 000 gezeigt. Weitere Informationen: https://lgrb-bw.de/geologie
-

Im Rahmen der Nutzung der Geothermie (Erdwärme) ist das LGRB als Genehmigungs- und Beratungsbehörde tätig und liefert wichtige, geowissenschaftliche Grundlageninformationen. Im Thema Geothermie werden eine Übersicht über die aktuell gemeldeten Erdwärmesonden und Wärmepumpen gegeben, die derzeitigen Geothermiekonzessionen gezeigt sowie Übersichtsdarstellungen der Temperaturverteilung in unterschiedlichen Tiefen gegeben. Weitere Informationen: https://lgrb-bw.de/geothermie
-

Im Rahmen des Projektes "Informationssystem Speichergesteine für den Standort Deutschland - eine Grundlage zur klimafreundlichen geotechnischen und energetischen Nutzung des tieferen Untergrundes (Speicher-Kataster Deutschland)" wurden von den staatlichen Geologischen Diensten der Bundesländer unter der Federführung der Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe nach bundesweit einheitlichen Kriterien Speicherpotenziale regional bewertet. Weitere Informationen:https://lgrb-bw.de/hydrogeologie
-

Eine wichtige Kompensationsmaßnahme bei Eingriffen in das Schutzgut Boden ist der fachgerechte Auftrag von geeignetem humosem Bodenmaterial in einer Mächtigkeit von rund 20 cm, der als Überschuss bei Baumaßnahmen anfällt. Zur Vorauswahl potenziell geeigneter Auftragsflächen werden zwei Layer zur Verfügung gestellt. 1. Suchräume für potenzielle Auftragsflächen zur Bodenverbesserung mit humosem Bodenmaterial: Die Karte wurde insbesondere für die Eigentümer und Bewirtschafter von Flächen, Vorhabenträger, Kommunen und Planungsbüros erstellt. Bei der Erstellung der Karten wurden bereits die wichtigsten fachlichen und rechtlichen Ausschlusskriterien berücksichtigt. 2. Bodendaten zur Ermittlung potenzieller Auftragsflächen zur Bodenverbesserung mit humosem Bodenmaterial: In der Karte werden ausschließlich die bodenkundlichen Grundlagen zur Auswahl von potenziellen Auftragsflächen zur Bodenverbesserung mit humosem Bodenmaterial beschrieben. Eine Berücksichtigung weiterer Kriterien aus dem Bereich des Naturschutzes und der Wasserwirtschaft findet hier nicht statt.
-
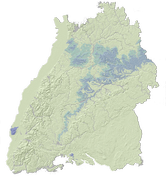
Die vorliegende Auswertung zeigt für Baden-Württemberg die geogenen Hintergrundkonzentrationen einer Vielzahl von Grundwasserinhaltsstoffen in Abhängigkeit von den durchflossenen Gesteinen. Sie liefert damit die Grundlage für die Definition von Warnwerten, Grenzwerten und Sanierungszielen in Regelwerken, in der Gesetzgebung und für die Praxis.
-

Mit der Überarbeitung und Fortschreibung der Aquiferstudie der Lockergesteine im baden-württembergischen Teil des Oberrheingrabens wird der derzeitige Kenntnisstand über die hydrogeologischen Grundlagen erstmals zusammenfassend in digitaler Form bereitgestellt. Das Arbeitsgebiet umfasst das Verbreitungsgebiet der pliozänen und quartären Kiese und Sande, die den bedeutendsten Grundwasserleiter Baden-Württembergs bilden. Die Darstellung der Einzelthemen ist maßstabsabhängig. Themen mit einem hohen Detaillierungsgrad und Datenmenge werden erst in größeren Maßstäben angezeigt. Die Ergebnisse der Auswertung sind in den LGRB-Informationen 19 - "Hydrogeologischer Bau und Aquifereigenschaften der Lockergesteine im Oberrheingraben Baden-Württemberg" (https://produkte.lgrb-bw.de/schriftensuche/lgrb-informationen/informationen19/?aid=78) - ausführlich beschrieben.
-
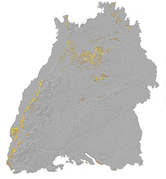
Direkte Sonnenstrahlung. Der Teil der Sonnenstrahlung, der die Erdatmosphäre ungehindert durchdringt und auf der Bodenoberfläche ankommt. Sie hat bei wolkenlosem Himmel den höchsten Wert. Zusammen mit der diffusen Sonnenstrahlung bildet sie die Globalstrahlung. In der Karte ist die Energiesumme pro Quadratmeter für die beiden Reifemonate September und Oktober dargestellt. Die auf der Bodenoberfläche ankommende direkte Sonnenstrahlung ist in unseren Breiten auf südlich ausgerichteten Lagen bei ca. 55 Prozent Hangneigung (ca. 30 Grad) übers Jahr gesehen am höchsten. Betrachtet man nur die beiden Reifemonate September und Oktober mit der dann schon tiefer stehenden Sonne, werden die höchsten Werte an extremen Steilhängen mit ca. 150 Prozent Hangneigung (ca. 55 Grad) erreicht. Weitere Informationen: https://lgrb-bw.de/bodenkunde/projekte/weinbauatlas
 Metainformationssystem GDI-BW
Metainformationssystem GDI-BW